Use SSH to connect the virtual machine on cloud and run jupyter notebook on it
In this blog, I will introduce how to create a virtual machine on openstack (it's a cloud platform), and then using SSH to connect the virtual machine with local computer. After the connection, I will show how to run jupyter notebook on this remote virtual machine.
(1) Create a SSH-keypair on openstack
The only method allowed to access the cloud instances is via ssh-keypairs. Username/Password is disabled by default on all cloud instances (according to best practice) and should never be enabled for security reasons.
The OpenStack software helps us create/import keys, and will make sure that the public keys are injected in the instances you create. The private key should be private and is for us to safekeep on our clients.
In the OpenStack dashboard: Compute -> Key Pairs -> Create Key Pair
Save the downloaded .pem file in a secure location on computer. We would need it when we want to access the virtual machine instance but we don't need to create a new ssh-keypair each time. 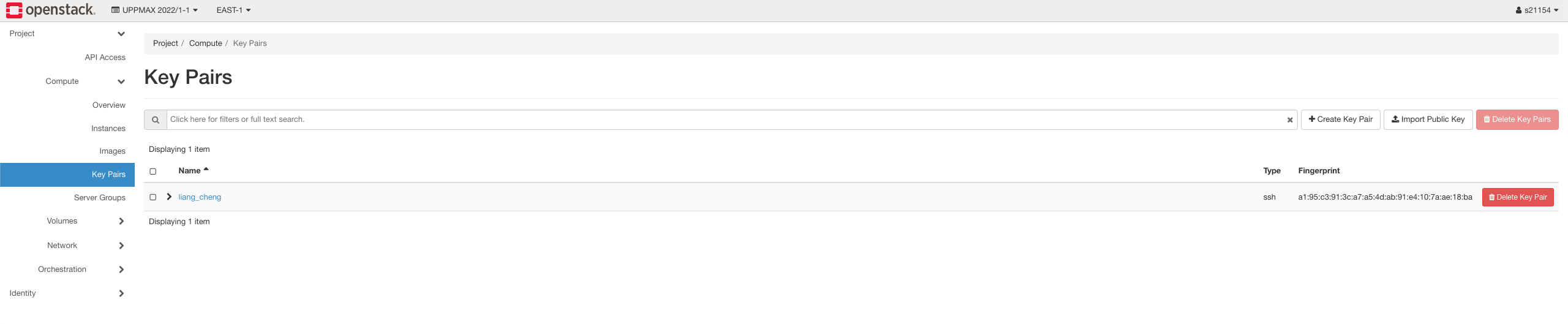
(2) Launch an instance of virtual machine on openstack
In the OpenStack dashboard: Compute -> Instances -> Launch instance
Then we can choose the configuration we want for the virtual machine. For my instance, I choose ubuntu 20.04 as the image, 1 VCPUS, 512 MB RAM and 20 GB disk. We also have to give this instance a name, and it would auto select to use the key-pair we create. As for the rest of the configuration, I chose the default for them. 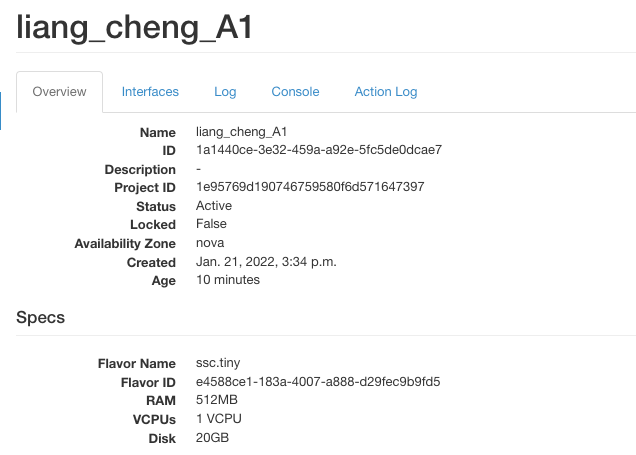
(3) Use SSH to access the virtual machine from local computer
Before the SSH connection, we need to associate a floating IP to the instance, which represents the IP address of this virtual machine. After the IP setting, we should change the permission of the downloaded-keypair file and SSH file so that the IP can access the key and connect with local computer. Run the following commands in terminal to change permission. "/..." is the path of this file on your computer.
1 | |
After the permission-change, we are able to use SSH to access the virtual machine by running the commands below.
1 | |

(4) Install jupyter notebook and run it on the virtual machine
Firstly, we need to install pip and jupyter notebook on the virtual machine.
1 | |
Then we edit the config file of jupyter notebook so that we can remotely log in it on the local browser.
1 | |
After everything is set up, we can run jupyter notebook.
1 | |
All articles in this blog adopt the CC BY-SA 4.0 agreement except for special statements. Please indicate the source for reprinting!